IELTS Reading: Matching Heading tips - Mẹo dự đoán nội dung từ headings
Bài thi Matching Headings (ghép tiêu đề) là dạng bài xuất hiện phổ biến trong bài thi IELTS Reading. Một số thí sinh gặp khó khăn trong việc xác định tiêu đề đúng, dù đã áp dụng các bước làm bài thường được gợi ý. Bài viết này sẽ giới thiệu về Matching Heading tips - kỹ thuật dự đoán nội dung từ headings, giải thích chi tiết cách áp dụng qua các ví dụ cụ thể, để từ đó giúp thí sinh cải thiện khả năng chọn tiêu đề đúng trong dạng bài Matching Headings.
Matching Heading tips - Mẹo dự đoán nội dung
Ngoài các 4 bước làm bài cơ bản, để nhận diện tiêu đề phù hợp nhanh hơn và chính xác hơn thí sinh nên kết hợp thêm Matching Heading tips - Kỹ thuật dự đoán nội dung. Kỹ thuật này sẽ “ngược” với cách làm bài thông thường, thay vì dự đoán tiêu đề cho đoạn văn, thí sinh sẽ dự đoán nội dung đoạn văn theo tiêu đề.
Cụ thể, trước khi bắt đầu đọc bài khóa, thí sinh nên đọc danh sách các tiêu đề để dự đoán, brainstorm nhanh xem một đoạn văn có tiêu đề này sẽ chứa các loại thông tin gì. Bước này sẽ giúp thí sinh định hình sơ bộ được nội dung của bài khóa, từ đó nhận diện nhanh hơn tiêu đề phù hợp khi bắt đầu đi vào đọc từng đoạn văn.
Matching Heading tips - 3 bước để dự đoán nội dung từ tiêu đề như sau:
Bước 1: Đọc từng tiêu đề (headings) và gạch chân các từ khóa.
Bước 2: Dự đoán các thông tin liên quan đến từ khóa. Có thể ghi nhanh sang bên cạnh tiêu đề các dự đoán.
Bước 3: Đọc lần lượt từng đoạn văn, tìm ý chính/câu chủ đề và đối chiếu với danh sách các tiêu đề và dự đoán đã đưa ra trước đó
Phần tiếp theo của bài viết sẽ tập trung phân tích bước 2 thông qua các ví dụ cụ thể để giúp người đọc hiểu rõ hơn về cách tư duy dự đoán nội dung bài khóa từ tiêu đề.
Áp dụng Matching Heading tips vào giải đề IELTS Reading
Ví dụ 1:
Personalities
(nguồn: Englobex)
List of Headings
i A degree of control
ii Where research has been carried out into the effects of family on personality
iii Categorising personality features according to their origin
iv A variety of reactions in similar situations
v A link between personality and aspects of our lives that aren’t chosen
vi A possible theory that cannot be true
vii Measuring personality
viii Different types of personality
ix How our lives can reinforce our personalities
x Potentially harmful effects of personality tests
Bước 1: Tìm từ khóa và dự đoán các dạng thông tin liên quan tới từ khóa
i A degree of control
Từ khóa: control (kiểm soát)
Bước 2: Dự đoán các thông tin liên quan đến từ khóa
Dự đoán nội dung đoạn văn: Sự kiểm soát tính cách của bản thân hoặc thao túng tính cách của người khác
Làm tương tự với các tiêu đề còn lại:
ii Effects of family on personality
Từ khóa: effects, family (ảnh hưởng, gia đình)
Dự đoán nội dung đoạn văn: Đoạn văn có thể sẽ nói tới ảnh hưởng của gia đình và việc nuôi dưỡng quá trình hình thành tính cách, ví dụ con cái thường giống tính cách bố mẹ, anh chị em ruột có tính cách giống nhau.
iii Categorising personality features according to their origin
Từ khóa: categorising, origin (phân loại, nguồn gốc)
Dự đoán nội dung đoạn văn: Đoạn văn có thể sẽ liệt kê các nét tính cách khác nhau tương ứng với các nguồn gốc khác nhau (có thể liên quan đến mã gen hoặc cách được nuôi dạy từ nhỏ)
iv A variety of reactions in similar situations
Từ khóa: variety, reactions, similar situations (đa dạng, phản ứng, tình huống giống nhau)
Dự đoán nội dung đoạn văn: Đoạn văn có thể sẽ liệt kê 1 số phản ứng khác nhau trong 1 tình huống
v A link between personality and aspects of our lives that aren’t chosen
Từ khóa: link, not chosen (sự liên kết, không được chọn)
Dự đoán nội dung đoạn văn: Đoạn văn có thể sẽ nhắc đến các yếu tố trong cuộc sống mà 1 người không thể lựa chọn như quê quán, chủng tộc, màu da, tầng lớp xã hội..
vi A possible theory that cannot be true
Từ khóa: theory, not true (thuyết, không đúng)
Dự đoán nội dung đoạn văn: Đoạn văn có thể sẽ nhắc đến 1 thuyết về tính cách đã bị phủ nhận
vii Measuring personality
Từ khóa: measuring (đo lường)
Dự đoán nội dung đoạn văn:
viii different types of personality
Từ khóa: types (các loại)
Dự đoán nội dung đoạn văn: Đoạn văn có thể sẽ liệt kê, mô tả các loại tính cách khác nhau như hướng nội, hướng ngoại, nhạy cảm…hoặc so sánh giữa cách những người có tính cách khác nhau phản ứng với 1 tình huống
ix how our life can reinforce our personalities
Từ khóa: reinforce (củng cố)
Dự đoán nội dung đoạn văn: Đoạn văn có thể sẽ cho thấy cách các lựa chọn được đưa ra khi người ta dần lớn lên khiến các tính cách rõ nét hơn, ví dụ như một người hướng ngoại hay đi giao lưu bạn bè sẽ trở nên càng hướng ngoại hơn.
x potentially harmful effects of personality tests
Từ khóa: harmful effects, tests
Dự đoán nội dung đoạn văn: Các bài test tính cách và cách ảnh hưởng tiêu cực đến người làm test như khiến họ hoài nghi về bản thân hay có các định kiến về người khác
Bước 3: Sau khi xem qua một lượt danh sách tiêu đề, thí sinh nên đọc từng đoạn văn trong bài khóa, tìm câu chủ đề và lần lượt đối chiếu với danh sách các tiêu đề và dự đoán đã đưa ra trước đó.
A We are all familiar with the idea that different people have different personalities, but what does this actually mean? It means that different people behave in different ways but it must be more than that. After all, different people find themselves in different circumstances, and much of their behaviour follows from this fact. However, our common experience reveals that different people respond in quite remarkably different ways even when faced with roughly the same circumstances. Alan might be happy to live alone in a quiet and orderly cottage, go out once a week, and stay in the same job for thirty years, whilst Beth likes nothing better an exotic travel and being surrounded by vivacious friends and loud music.
-> Tiêu đề tương ứng: iv
Câu chủ đề và từ khóa tương ứng tiêu đề iv: “... different people respond in quite remarkably different ways even when faced with roughly the same circumstances.”
Đoạn thông tin trùng với dự đoán: “Alan might be happy to live alone in a quiet and orderly cottage, go out once a week, and stay in the same job for thirty years, whilst Beth likes nothing better an exotic travel and being surrounded by vivacious friends and loud music”
B In cases like these, we feel that it cannot be just the situation which is producing the differences in behaviour. Something about the way the person is ‘wired up’ seems to be at work, determining how they react to situations, and, more than that, the kind of situations they get themselves into in the first place. This is why personality seems to become stronger as we get older; when we are young, our situation reflects external factors such as the social and family environment we were born into. As we grow older, we are more and more affected by the consequences of our own choices (doing jobs that we were drawn to, surrounded by people like us whom we have sought out). Thus, personality differences that might have been very slight at birth become dramatic in later adulthood.
-> Tiêu đề tương ứng: ix
Câu chủ đề và từ khóa tương ứng tiêu đề: “...personality seems to become stronger as we get older…”, “...personality differences that might have been very slight at birth become dramatic in later adulthood.”
Đoạn thông tin trùng với dự đoán: như câu chủ đề nêu trên.
C Personality, then, seems to be the set of enduring and stable dispositions that characterise a person. These dispositions come partly from the expression of inherent features of the nervous system, and partly from learning. Researchers sometimes distinguish between temperament, which refers exclusively to characteristics that are inborn or directly caused by biological factors, and personality, which also includes social and cultural learning. Nervousness, for example, might be a factor of temperament, but religious piety is an aspect of personality.
-> Tiêu đề tương ứng: iii
Câu chủ đề và từ khóa tương ứng tiêu đề iii: “Researchers sometimes distinguish between temperament, which refers exclusively to characteristics that are inborn or directly caused by biological factors, and personality, which also includes social and cultural learning”
Đoạn thông tin trùng với dự đoán: “Nervousness, for example, might be a factor of temperament, but religious piety is an aspect of personality.”
D The discovery that temperamental differences are real is one of the major findings of contemporary psychology. It could easily have been the case that there were no intrinsic differences between people in temperament, so that given the same learning history, the same dilemmas, they would all respond in much the same way. Yet we now know that this is not the case.
-> Tiêu đề tương ứng: vi
Câu chủ đề và từ khóa tương ứng với từ khóa trong tiêu đề vi: “ ...one of the major findings...”, “Yet we now know that this is not the case.”
Đoạn thông tin trùng với dự đoán: như câu chủ đề nêu trên.
E Personality measures turn out to be good predictors of your health, how happy you typically are – even your taste in paintings. Personality is a much better predictor of these things than social class or age. The origin of these differences is in part innate. That is to say, when people are adopted at birth and brought up by new families, their personalities are more similar to those of their blood relatives than to the ones they grew up with.
-> Tiêu đề tương ứng: ii
Câu chủ đề và từ khóa tương ứng với từ khóa trong tiêu đề ii: “The origin of these differences is in part innate.”
Đoạn thông tin trùng với dự đoán: “...their personalities are more similar to those of their blood relatives than to the ones they grew up with”
F Personality differences tend to manifest themselves through the quick, gut-feeling, intuitive and emotional systems of the human mind. The slower, rational, deliberate systems show less variation in output from person to person. Deliberate rational strategies can be used to override intuitive patterns of response, and this is how people wishing to change their personalities or feelings have to go about it. As human beings, we have the unique ability to look in at our personality from the outside and decide what we want to do with it.
-> Tiêu đề tương ứng: i
Câu chủ đề và từ khóa tương ứng với từ khóa trong tiêu đề i: “Deliberate rational strategies can be used to override intuitive patterns of response, and this is how people wishing to change their personalities or feelings have to go about it.”
Đoạn thông tin trùng với dự đoán: như câu chủ đề nêu trên.
Ví dụ 2: Gợi ý: Đầu tiên, người đọc nên thử áp dụng các bước phân tích, dự đoán như trên để tự chọn đáp án trước, sau đó check hướng dẫn ở dưới.
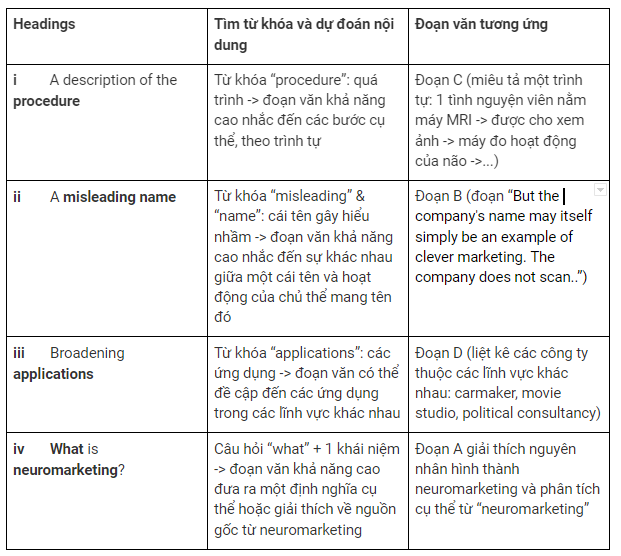
List of headings
i A description of the procedure
ii A misleading name
iii Broadening applications
iv What is neuromarketing?
Inside the mind of the consumer
(nguồn: http://mini-ielts.com/)
Could brain-scanning technology provide an accurate way to assess the appeal of new products and the effectiveness of advertising?
A
MARKETING people are no longer prepared to take your word for it that you favour one product over another. They want to scan your brain to see which one you really prefer. Using the tools of neuroscientists, such as electroencephalogram (EEG) mapping and functional magnetic-resonance imaging (fMRI), they are trying to learn more about the mental processes behind purchasing decisions. The resulting fusion of neuroscience and marketing is inevitably being called 'neuromarketing’.
B
The first person to apply brain-imaging technology in this way was Gerry Zaltman of Harvard University, in the late 1990s. The idea remained in obscurity until 2001, when BrightHouse, a marketing consultancy based in Atlanta, Georgia, set up a dedicated neuromarketing arm, BrightHouse Neurostrategies Group. (BrightHouse lists Coca-Cola, Delta Airlines and Home Depot among its clients.) But the company's name may itself simply be an example of clever marketing. BrightHouse does not scan people while showing them specific products or campaign ideas, but bases its work on the results of more general fMRI-based research into consumer preferences and decision-making carried out at Emory University in Atlanta.
C
Can brain scanning really be applied to marketing? The basic principle is not that different from focus groups and other traditional forms of market research. A volunteer lies in an fMRI machine and is shown images or video clips. In place of an interview or questionnaire, the subject's response is evaluated by monitoring brain activity. fMRIprovides real-time images of brain activity, in which different areas “light up” depending on the level of blood flow. This provides clues to the subject's subconscious thought patterns. Neuroscientists know, for example, that the sense of self is associated with an area of the brain known as the medial prefrontal cortex. A flow of blood to that area while the subject is looking at a particular logo suggests that he or she identifies with that brand.
D
At first, it seemed that only companies in Europe were prepared to admit that they used neuromarketing. Two carmakers, DaimlerChrysler in Germany and Ford's European arm, ran pilot studies in 2003. But more recently, American companies have become more open about their use of neuromarketing. Lieberman Research Worldwide, a marketing firm based in Los Angeles, is collaborating with the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) to enable movie studios to market-test film trailers. More controversially, the New York Times recently reported that a political consultancy, FKF Research, has been studying the effectiveness of campaign commercials using neuromarketing techniques.
Matching Heading tips - Hướng dẫn dự đoán và giải thích đáp án:
 Tổng kết
Tổng kết
Bài viết đã giới thiệu Matching Heading tips với kỹ thuật đoán nội dung từ tiêu đề thông qua các bài khóa cụ thể. Áp dụng kĩ thuật này với mỗi bài Matching Heading, thí sinh sẽ hiểu được cách các tiêu đề tóm tắt nội dung các đoạn văn. Thêm vào đó, việc làm quen với việc phán đoán nội dung từ tiêu đề sẽ giúp thí sinh đẩy nhanh tốc độ và tăng độ chính xác khi ghép tiêu đề, từ đó cải thiện điểm Reading.
Nguyễn Diệu Linh
Đọc thêm: IELTS Reading Matching Headings Tips: Cách loại trừ 4 bẫy đáp án thường gặp

Bình luận - Hỏi đáp